
Hard water is water that has high dissolved mineral content, including high concentrations of calcium (Ca2+) and magnesium (Mg2+) ions. High concentrations of calcium and magnesium ions in hard water can pose health risks, especially for individuals with kidney conditions. Hard water also leads to scale buildup, which damages pipes and appliances, reducing efficiency and increasing maintenance costs. Additionally, hard water negatively affects washing performance, requiring more detergent, and has an unpleasant taste. Softening the water improves taste, protects equipment, and enhances overall quality of life.
Resins play a crucial role in drinking water softening by utilizing ion exchange technology to remove hardness ions, such as calcium (Ca2+) and magnesium (Mg2+). This process improves water quality and extends the lifespan of pipes and equipment.

Drinking water softening is mainly adopt cation resins to remove Ca, Mg and other hardness ions. The cation resins can be divided into Strong Acid Cation (SAC) and Weak Acid Cation (WAC) resins.
The raw water (hard water) enters the softener and passes through the ion exchange resin charged with sodium (Na+) ions. As hard water passes through the resin, sodium ions will physically capture and exchange the hardness ions (Ca2+ & Mg2+) and release the Na+ ions. This process can continuously remove hardness ions and produce soft water for the whole-house water system. During this period, the resin becomes saturated with hardness ions and depleted of sodium ions along the softening process working. As the resin nears exhaustion, the regeneration cycle must be initiated.
2R−Na + Ca2+ → R2+−Ca + 2Na+
2R−Na + Mg2+ → R2+−Mg + 2Na+
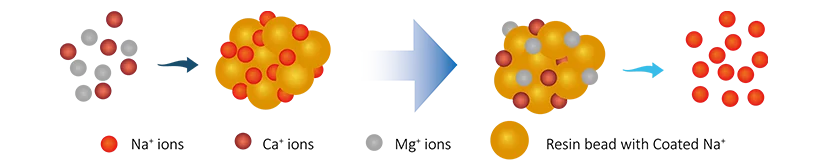
In that,
This process reduces water hardness, ensuring soft water for industrial applications.
During the regeneration cycle, brine (NaCl) water, generated in the brine tank by mixing water and salt is passed through the resin tank (either up or down depending on the design). As this brine passes through the tank, sodium (Na+) ions in the brine water are transferred (exchanged) to the exchange resins and these hardness ions (Ca2+ & Mg2+) are consequently sent to drain. This process continues until all the hardness ions are exchanged with the sodium ions. The resins are regenerated and can continue to soften waters again.
R2+−Ca + 2NaCl → 2R−Na + CaCl2
R2+−Mg + 2NaCl → 2R−Na + MgCl2
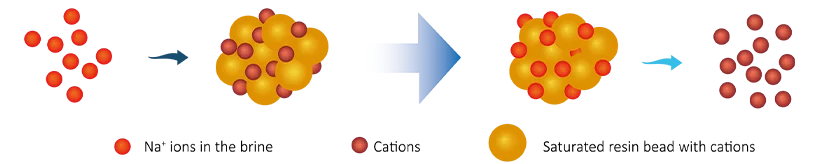
In that,
Regeneration restores the resin's ion exchange capacity, ensuring cost-effective and sustainable operation.
Water Softening System Benefits
Continuous softening water supply
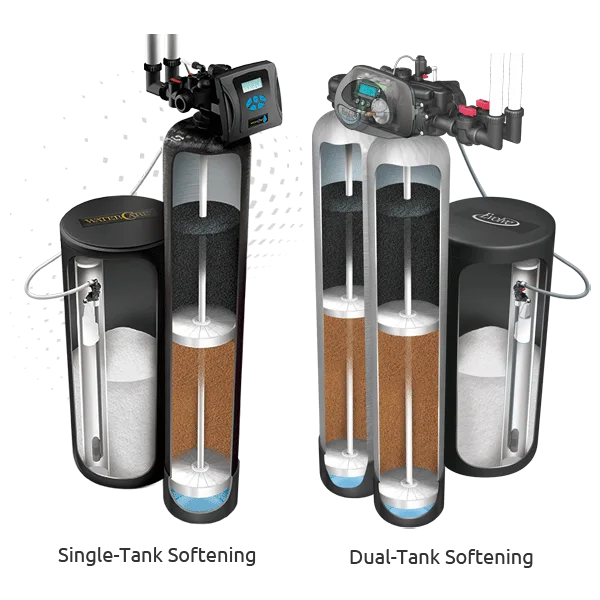
During resin generation period, the resins can not only work at the same time, that is, it can not supply softening water temporarily. You can choose the suitable solution to solve this problems.


No matter guides, inquiry or assistance, our experts are ready to serve you.