
During production and conveying, the condensate may be polluted by the following reasons: Silica, additional impurities, TDS and Iron or copper oxides.
Ion exchange resins are commonly employed in condensate treatment systems to remove dissolved ions, particularly those that contribute to water hardness and corrosion. These resins work by exchanging undesirable ions (such as calcium, magnesium, and other contaminants) with less problematic ions like sodium or hydrogen.

Sepurlite supplies various resin types for condensate water treatment application. The ion exchange resins are mainly used in the pre-treatment of condensate water treatment to remove large particles and suspended solids and they can be used in the polishing process (Mixed bed) for further treatment. All of these have excellent performance and long service life. You can choose appropriate cation and anion resins according to your specific conditions.
The condensate polishing is mainly completed relying on the ion exchange technology and they can be complete treatment in straight or spherical tank. It can produce qualified water with minimal impurities and almost zero leakage. The ion exchange mixed bed is mainly used in the condensate polishing to remove ion, dissolved carbon dioxide and suspended solids and colloids and other impurities.
There are two mixed bed types: hydrogen-type (H-OH) mixed bed and ammonia-type (NH4-OH) mixed bed.
In this system, the production water is pure water (H2O) and the pH range is natural or weak acid, which is suitable for nuclear industry and other occasions where natural ultra pure water quality is required.
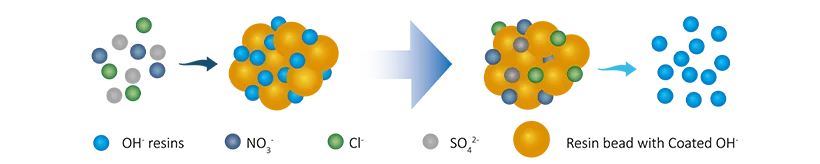
The R-H represents the cation resins and R-OH represents anion resins, the reactions are as follows:
Cation resins reaction:
R-H + Na+(Ca2+/Mg2+) → R-Na(Ca2+/Mg2+) + H+
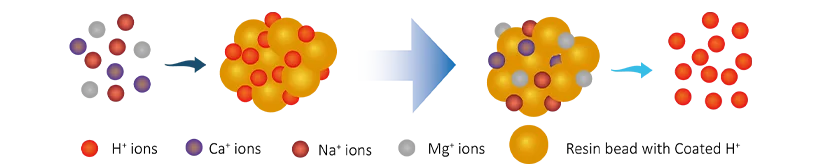
Anion resins reaction:
R-OH + Cl-(SO42-/NO3-/HSiO3-) → R-Cl(SO42-/NO3-/HSiO3-) + OH-
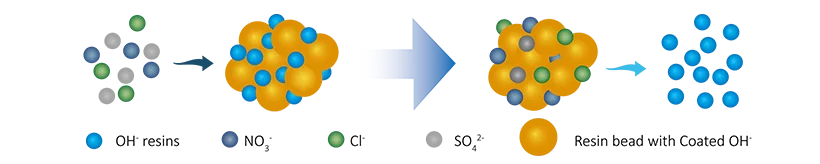
Final reaction:
R-H + R-OH +Na+ (Ca2+/Mg2+) + Cl-(SO42-/NO3-/HSiO3-) → R-Na + R-Cl + H2O
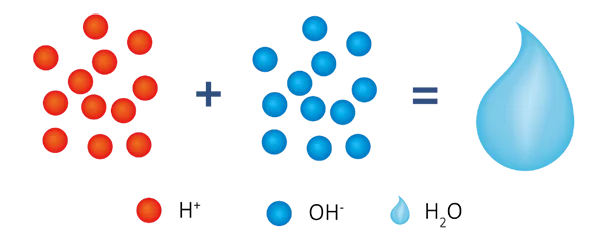
In this system, the production water is ammonia water (NH4OH) and the pH range is weak alkali, which can prevent equipment and pipeline from water acid corrosion and it is suitable for boiler water treatment and other occasions where alkali water quality is required.
The R-NH4 represents the cation resins and R-OH represents anion resins, the reactions are as follows:
Cation resins reaction:
R-NH4 + Na+(Ca2+/Mg2+) → R-Na(Ca2+/Mg2+) +NH4+
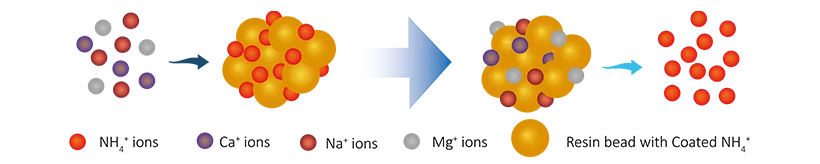
Anion resins reaction:
R-OH + Cl-(SO42-/NO3-/HSiO3-) → R-Cl(SO42-/NO3-/HSiO3-) + OH-
Final reaction:
R-NH4 + R-OH +Na+ (Ca2+/Mg2+) + Cl-(SO42-/NO3-/HSiO3-) → R-Na + R-Cl + NH4OH
Power Industry
Chemical Industry
Steel Industry
Pharmaceutical Industry
Food and Beverage Industry
Pulp and Paper Industry
Construction and HVAC Systems

No matter guides, inquiry or assistance, our experts are ready to serve you.