
Dissolved ions (such as calcium, magnesium, sodium, chloride, etc.) will have a serious impact on many industrial processes, water deionization is the best way to solve these problems. water deionization is a process to remove all dissolved ions and other impurities from the water using ion exchange resins. It is crucial in many sectors, from pharmaceuticals, labs to electronics where there has critical requirements on water purity.

We supply the best ion exchange resin types for water deionization applications. According to the selected deionization process, you can choose the suitable SAC and SBA resin types for your water treatment applications.
Ion exchange is the classical water deionzation method, it make full of the high ion exchange capacity to remove all dissolved ions in the water. The main process is as follows:
before entering the ion exchange tank, the raw water will be pre-treated to remove suspended matter, colloidal particles and organic matters. The common pre-treatment methods include sand filtration, activated carbon filtration and precision filtration. This pre-treatment can prevent impurities from clogging the ion exchange resins and extend their service life.
Pre-treated water flows through the cation resin tank, where there has cation resin tanks with hydrogen ions (H+). The dissolved cation ions (Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+) will be exchanged with H+, the ion exchange process is as follows:
R-H + Na+ → R-Na + H+
R-H + Ca2+ → R-Ca + 2H+
R-H + Mg2+ → R-Mg + 2H+
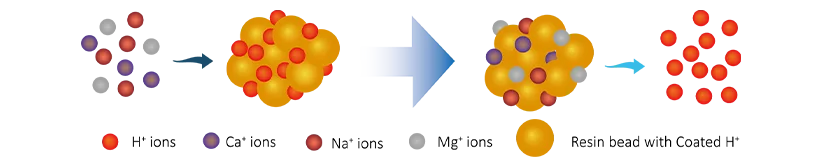
After that , the dissolved cation ions are removed and the content of H+ ions in the water increases.
Water flows through the anion resin tank, where there has anion resin tanks with hydroxide ion (OH-). The dissolved cation ions (Cl-, SO₄2-, CO₃2-) will be exchanged with OH-, the ion exchange process is as follows:
R-OH + Cl- → R-Cl + OH−
2(R-OH) + CO32- → (R2CO3) + 2OH-
2(R-OH) + SO42- → (R2SO4) + 2OH-
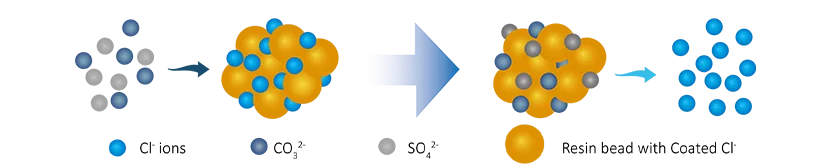
After that , the dissolved anion ions are removed and the content of OH- ions in the water increases.
After cation exchange and anion exchange, hydrogen ions (H⁺) and hydroxide ions (OH-) in water combine with each other to form water molecules (H₂O).
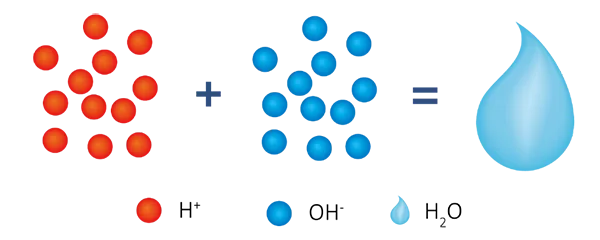
Through this process, most of the ions in the water are removed, producing high purity deionized water.
After a period of use, the ions on the resin are gradually exhausted and regeneration process is required.
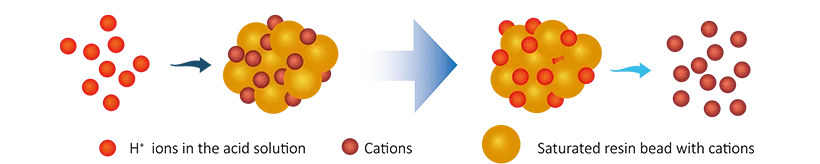
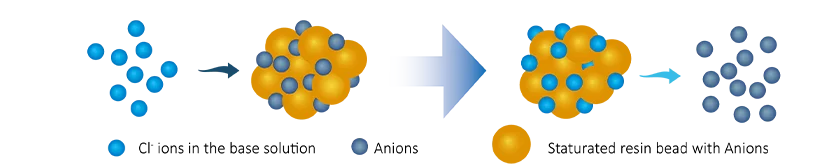
After regeneration, the resin is restored to its initial state and can continue to be used to remove ions from water.
Electronics & Semiconductor Manufacturing
Metal and Surface Treatment

No matter guides, inquiry or assistance, our experts are ready to serve you.