In condensate treatment, if the mixed bed resins are exhausted, they need to be regenerated for the following production. The regeneration of mixed bed resins are complex and the resin separation is the crucial to regeneration. The regeneration of the resin commonly adopts external regeneration. External regeneration means that ion exchange and resin regeneration are carried out in different equipment, which simplifies the internal structure of the high-speed mixed bed. There is no need to install acid and alkali pipelines on the mixed bed itself, which helps prevent accidental incidents where acid or alkali might enter the condensate water system, ensuring normal operation. Additionally, the resin is regenerated in a dedicated regenerator, which improves regeneration efficiency. The external regeneration system consists of a resin separation tower (SPT), an separation / anion resin regeneration tower (ART), a cation resin regeneration and storage tower (CRT), and related pumps, interface isolation vessel (IIV), blowers, etc.
Here is the detailed processes:
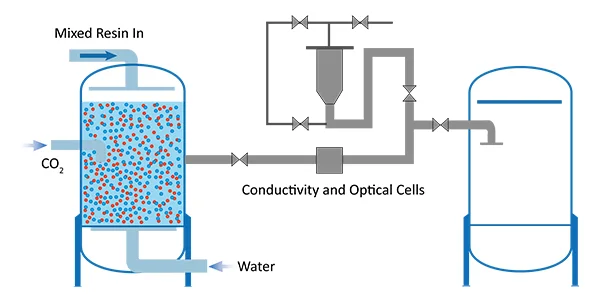
Mixed Bed → Separation / Anion Regeneration Tank

The exhausted mixed resins is transferred to the resin separation / anion regeneration tank (ART). Another small amount of mixed resins in the interface isolation vessel (IIV) is also transferred to the resin separation / anion regeneration tank. Then backwash and air sour the resins to remove particulates.
Backwash to Separate the Cation/Anion Resins

The resin is backwashed again without air scour and the denser cation resin sinks to the bottom of the tank. The interface is visible through a sight glass in the tank.
Transfer to Cation Regeneration Tank

Inject carbon dioxide carefully into the tank to transfer the cation resins into the second tank – Cation Regeneration Tank. The unique cone design of the tank bottom gradually reduces the diameter of the resin interface and directs it into the outlet branch.
Mixed Resins → Interface Isolation Vessel

Continuously transfer the cation resins until the conductivity difference of resin interface, close the transfer line and transfer the small amount of resins into interface insolation pot. If the conductivity cell failing, you can detect then via optional cells by color difference.
Regeneration

Regenerate the cation and anion resin simultaneously. The anion resins are regenerated with caustic soda and the cation resins are regenerated with acid solutions. Then rinse the resins and drain. If there is remaining some cation resins in the anion tanks, transfer them to the interface isolation pot.
Back to Mixed Bed

The regenerated anion resins are transferred to the cation regeneration tank, the two resins are rinsed and mixed to final quality, and then transferred back to the mixed bed for polishing service.